명월초에서 분리한 오이모자이크바이러스의 감염 첫 보고
First Report of Cucumber mosaic virus Isolated from Sambungai (Gynura procumbens)
Article information
Abstract
In March 2016, an isolate of Cucumber mosaic virus (named Gyp-CMV) was isolated from the Sambungai (Gynura procumbens) showing the symptoms of mosaic and chlorosis. The isolate Gyp-CMV was characterized by disease reactions in several indicator plants, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism, and sequence analysis of movement protein (3a) and coat protein (CP) genes. Tobacco, tomato, pepper, ground cherry, and lambsquarters (Chenopodium quinoa and C. amaranticolor) appeared typical CMV symptoms, but zucchini and cucumber were not infected. Phylogenetic analysis of the 3a and CP gene indicated that Gyp-CMV belongs to the CMV subgroup II. Sequence identities of the Gyp-CMV 3a and CP genes showed 99.3% and 100% to that of Hnt-CMV at amino acid level. To our knowledge, this is the first report of CMV infection in Gynura procumbens.
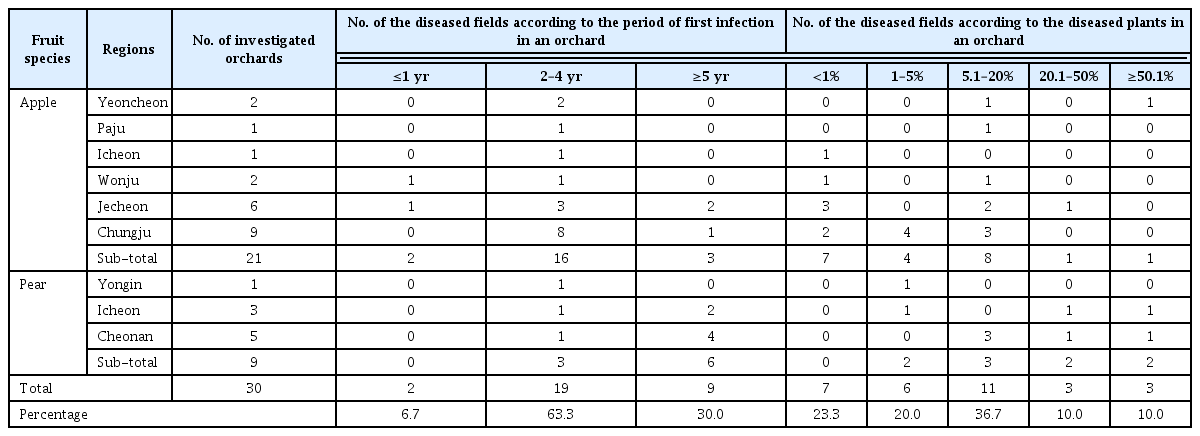
오이모자이크바이러스(Cucumber mosaic virus, CMV)는 Bromoviridae과, Cucumovirus 속에 속하며, 직경 29 nm의 구형으로 되어 있고, 85과 1,000종 이상의 매우 넓은 기주범위를 갖는다(Palukaitis 등, 1992). 전 세계적으로 널리 분포하고 많은 종류의 작물에 피해를 주고 있는 식물바이러스로 채소나 화훼에서는 가장 중요한 병원체의 하나이다(Tomlinson, 1987). CMV는 3개의 게놈과 2개의 서브게놈을 가지며(Wang 등, 2002), 다양한 식물에서 발견되는 만큼 계통 또는 분리주(isolate) 간에도 유전적 다양성이 큰 것으로 알려져 있다(Owen과 Palukaitis, 1988). 지금까지 보고된 CMV는 기주 반응의 특성과 혈청학적 분석, 외피단백질의 서열과 RT-PCR을 이용한 외피단백질 유전자의 제한효소 절단패턴 분석 등에 따라 subgroup I과 II로 구분되며(Choi 등, 1990, 1999; Owen과 Palukaitis, 1988; Wahyuni 등, 1992). subgroup I 계통의 CMV의 경우 RNA3의 외피단백질 유전자와 5’ 비번역 부위를 통하여 subgroup IA와 subgroup IB로 세분화하였다(Roossinck 등, 1999). 국내의 경우 2007년부터 2011년까지 5년간 주요 작물 바이러스병 검정비율을 분석한 결과 CMV가 가장 높은 검정률을 나타내어 농가에 피해를 끼치는 것으로 보고되었다(Kim 등, 2012).
명월초는(Gynura procumbens) 국화과에 속하는 여러해살이 식물이며, 태국, 인도네시아, 한국 등지에서 재배되고 있다(Hassan 등, 2010). 최근 발열, 발진, 신장질환, 편두통, 변비, 고혈압, 당뇨병 및 함암에 효과가 있는 것으로 보고되어 있다 (Rosidah 등, 2009). 우리나라에서는 Broad bean wilt Virus 2 (BBWV2)가 명월초에서 보고되어 있으며(Kwak 등, 2017), 아직까지 다른 바이러스의 감염보고 및 동정은 전무한 실정이다. 본 연구에서는 2016년 3월 춘천농업기술원에 위치한 유리온실에서 모자이크와 황화병징(Fig. 1)을 보이는 명월초로부터 바이러스를 분리하여 CMV-Gyp로 명명하고, RT-PCR 진단 및 이동단백질과 외피단백질 유전자 염기서열 분석을 통하여 명월초에서 CMV를 동정하였다.

Symptoms caused by Cucumber mosaic virus isolate Gyp (Gyp-CMV) in the greenhouse. (A) Gynura procumbens, (B) Enlarge of A. plant showed mosaic and chlorotic spot.
기주식물반응
바이러스에 감염된 명월초의 상엽을 채집하여 Nicotiana benthamiana에 즙액접종을 실시하였다. 접종 12일 후 N. benthamiana로 부터 Chenopodium quinoa에 접종하여 단일병반을 분리하였다. N. benthamiana외 4종의 담배(N. tabacum cv. Xanthi nc, cv. Samsun nn, N. glutinosa 및 N. rustica)와 Chenopodium quiona, C. amaranticolor, Cucumis sativus cv. Baek Dadagi, Cucurbita pepo cv. Black beauty, Physalis floridana, Capsicum annuum cv. Cheong yang, Vigna unguiculata에 접종한 결과 오이와 쥬키니호박의 경우 상엽에서 감염되지 않는 특성을 보였다(Table 1). 이러한 결과는 다양한 기주에서 분리된 CMV가 서로 다른 기주특이성을 가지고 있는 것으로 추정되었다.
RT-PCR 및 제한효소지도
기주식물 반응을 통해 명월초에 감염된 바이러스가 CMV의 한 계통으로 추정되어 Cucumovirus에 속한 바이러스 검정 프라이머(Table 2; Choi 등, 1999)를 이용하여 대조구인 Fny-CMV (Subgroup IA), As-CMV (Subgroup IB), Ls-CMV (Subgroup II)와 함께 RT-PCR 진단을 수행하였다. 증폭된 RT-PCR 산물의 전기영동 결과, 대조바이러스(Fny-, As- 및 Ls-CMV)와 같은 크기의 증폭산물을 확인할 수 있었다(Fig. 2). 이 결과로부터 명월초에 감염된 바이러스가 CMV의 한 계통인 Gyp-CMV로 명명하여 실험을 수행하였다. Gyp-CMV의 특성과 계통분석을 위해 EcoR I, Hind III, Sal I 등 제한효소를 사용하여 RT-PCR 산물에 대한 PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) 분석을 실시하였다. 그 결과 CMV의 서브그룹 구분이 가능한 EcoR I에서 Gyp-CMV는 Ls-CMV와 같은 패턴으로 증폭산물이 절단되지 않았으나 Fny-CMV는 절단되지 않는 특성을 보였다(Fig. 2). 이는 Gyp-CMV가 CMV Subgroup II의 한 계통인 것으로 확인할 수 있었다.

Cucumber mosaic virus detection (A) and PCR-RFLP analysis (B) of Cucumber mosaic virus isolate Gyp using the Cucumovirus genus specific primer sets. Lane 1, Gyp-CMV; Lane 2, Fny-CMV; Lane 3, As-CMV; Lane 4, Ls-CMV; H, healthy plant as a control; M, size marker(100bp DNA ladder). Restriction pattern of three CMVs on 1.2% agarose gel. M, size marker(100bp DNA ladder); lane 1, uncut; lanes 2, 5, and 8, Gyp-CMV; lanes 3, 6, and 9, Fny-CMV; lanes 4, 7, and 10, Ls-CMV; lanes 2-4, Eco RI; lanes 5-7, Hind III; lanes 8-10, Sal I; CMV, Cucumber mosaic virus.
염기서열 및 계통도분석
Gyp-CMV RNA3에 존재하는 이동단백질과 외피단백질 영역의 염기서열 분석을 위하여 Table 2에 제시된 프라이머를 활용하였다. RT-PCR 증폭산물에 대한 크기 및 염기서열 분석 결과 각각 889, 1,433개의 염기서열을 확인할 수 있었다. 결정된 이동단백질 및 외피단백질 염기서열은 NCBI GenBank에 각각 등록하였다(accession no. MG273137 및 MG273138) 이동단백질과 외피단백질 영역에 대한 아미노산서열을 바탕으로 NCBI GenBank에 보고되어 있는 CMV 11분 리주와 비교한 결과 Hnt-CMV 분리주와 99.3%, 100%의 상동성을 보였으며, 분자계통분석(MEGA6 software)을 실시한 결과 Gyp-CMV는 CMV Subgroup II 계통들과 유연관계가 높게 나타남을 확인할 수 있었다(Fig. 3). 이러한 결과를 통하여 명월초에서 CMV의 감염을 최초로 확인하였다.
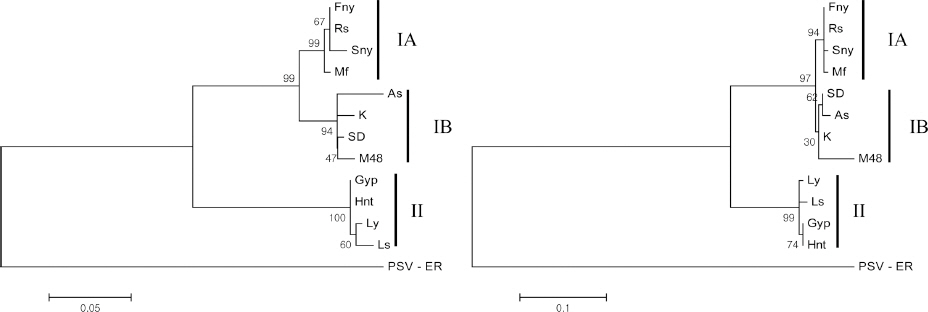
Phylogenetic analysis of 3a protein (A) and coat protein (B) of Cucumber mosaic virus isolate Gyp and used species of 12 Cucumovirus. The abbreviations of virus names and GenBank accession number used in the phylogenetic tree analysis: Fny-CMV (D10538.1), Sny-CMV (U66094.1), Mf-CMV (AJ276481.1), Rs-CMV (AJ517802.1), As-CMV (AF013291.1), M48-CMV (D49496.1), K-CMV (AF127977.1), SD-CMV (AB008777.1), Hnt-CMV (KC407999.1), Ly-CMV (AF198130.1), Ls-CMV (AF127976.1), ER-PSV (NC002040.1). Phylogenetic trees were bootstrapped using 1,000 replications. Also, they were performed employing the maximum likehood method packaged in the MEGA6 software.
요약
2016년 3월, 모자이크와 황화 병징을 보이는 명월초 잎에서 CMV를 분리하여 CMV-Gyp로 명명하였다. 기주식물의 생물적 반응과 RT-PCR, PCR-RFLP, 이동단백질 및 외피단백질 유전자의 염기서열 분석을 통해 CMV를 동정하였다. 가지과(담배, 고추, 꽈리)와 비름과(흰명아주, 붉은명아주)에서는 전형적인 CMV의 병징이 나타났으나 박과(쥬키니호박, 오이)에서는 병징이 발현되지 않는 특성을 보였다. 3a 및 CP 유전자의 계통학적 분석 결과, CMV-Gyp가 CMV Subgroup II에 속하는 것으로 나타냈다. CMV-Gyp의 이동단백질과 외피단백질유전자의 서열은 아미노산 수준에서 CMV-Hnt와 99.3% 및 100% 일치하였다. 이 논문은 명월초에서 CMV 감염에 대한 첫 보고이다.
Acknowledgement
This study was carried out with the support of Cooperative Research Program for Agricultural Science & Technology Development (Project No. PJ012266012017 and PJ010878042017) in Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea, basic science Research Program through the NRF funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2017R1D1A1B03036553) and 2015 Research Grant from Kangwon National University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing and commercial interests in this work.