벼검은줄오갈병바이러스 외피단백질 유전자 단백질 발현과 항혈청 제작
In Vitro Expression and Antibody Preparation of Rice black-streaked dwarf virus Coat Protein Gene
Article information
Abstract
본 연구에서는 RBSDV의 외피단백질 P10을 코드하는 S10을 E. coli에서 발현시켰다. RBSDV-miryang isolate (GenBank JX994211)로부터 추출한 게놈 dsRNA을 주형으로 S10의 특이적인 primer를 사용하여 P10의 N-말단영역(1-834 nt, 1-278 aa)을 RT-PCR에 의해 증폭하였다. 증폭된 RBSDV S10-N (1-834 nt)을 발현 벡터 pET32a(+)에 클로닝하여 E. coli BL21(DE3)에서 발현시킨 후 Ni-NTA affinity column으로 발현된 단백질을 정제하였다. 정제된 단백질을 면역 동물에 주사하여 항혈청을 제작하였다. 제작된 항혈청은 Western blot 및 ELISA 분석으로 RBSDV와의 특이성을 확인하였다. 본 연구에서 RBSDV 한국 isolate의 항혈청이 제작되었으며 금후 혈청학적 연구의 좋은 재료로 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대한다.
Trans Abstract
In this work, major outer capsid protein (P10) encoded by genome segment S10 of Rice black-streaked dwarf virus (RBSDV) was expressed in Escherichia coli. Genomic dsRNA was extracted from RBSDV-miryang isolate infected rice plants. Based on the sequence of S10 (RBSDV-miryang, GenBank JX994211), a pair of S10 specific primers were designed and used to amplify the fragment encoding the N-part of P10. We amplified the partial gene (S10 1-834 nt) of RBSDV P10 (1-278 aa) by RT-PCR. Amplified RBSDV S10 (1-834 nt) was cloned into the expression vector pET32a (+). Recombinant RBSDV S10 (1-834 nt) was expressed in E. coli BL21(DE3) and purified by nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid (Ni-NTA) affinity column. We successfully obtained P10 partial protein of RBSDV and the purified protein was used to immunize rabbits. The resulting polyclonal antiserum specifically recognized RBSDV from infected plant in both Western blotting and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. In this study, we provide purified RBSDV P10 (1-278 aa), which would be good material for the serological study of RBSDV-miryang isolates.
서론
벼검은줄오갈병(Rice black-streaked dwarf virus, RBSDV)은 Reoviridae과의 Fijivirus속에 속하고 벼, 옥수수, 보리, 밀 등을 기주로 하며, 애멸구(Laodelphax striatellus)에 의해 충매전염된다(Shikata와 Kitagawa, 1977; Wang 등, 2003). 게놈은 dsRNA로 S1–S10의 10분절로 이루어져 있으며 2001년 10분절의 염기서열이 모두 결정되었다(Fang 등, 2001; Zhang 등, 2001). 벼의 RBSDV는 우리나라, 일본, 중국에서 발생이 보고되었으며, 일본에서는 1941년에, 우리나라와 중국에서는 1960년대에 대발생한 적이 있다(Isogai 등, 2001; Shikata와 Kitagawa, 1977). 우리나라에서 RBSDV의 발생은 1970년대 이후 감소하기 시작하여 2000년도까지 현저히 줄어들었지만 최근 들어 상습 발생지였던 남부 및 중부지역의 벼 재배지에서 RBSDV의 발생이 재확인되었다(Lee 등, 2005, 2006). 2005년도에는 지금까지 발생이 없었던 전북 고창에서 발생이 확인되었으며 영덕, 울진에서 발생이 확대되는 경향을 보이고 있다(Lee 등, 2005). 2004년 고창의 발병이 심한 포장의 경우 약 80%의 발병률을 나타내기도 하였으며, 2005년 고창의 줄무늬 및 위축증상을 나타내는 옥수수 감염주로부터 병원 바이러스가 RBSDV임을 확인하였다(Lee 등, 2005, 2006). 아직까지 RBSDV에 대해서는 저항성 품종이 없으므로 한번 발생하면 벼농사에 큰 피해를 입게 된다. 방제방법으로는 애멸구 월동충의 보독충률 검정을 통해 발생을 예측하여 애멸구를 방제하고, 옥수수 파종기 또는 벼 이앙시기 조절 등을 통한 경종적인 방제 등이 있다(Lee 등, 1989). RBSDV 진단을 위해 일반적으로 RT-PCR이 사용되고 있으나 애멸구 보독충률 검정 등의 대량 검정에 사용하기에는 번거롭고 진단비용이 비싼 단점이 있다. RBSDV는 식물체 내의 사부조직에 국한하여 존재하므로 항체 제작에 충분한 양의 바이러스를 얻기가 쉽지 않고, 바이러스 입자의 분리 과정에서 입자가 쉽게 파괴되기 때문에 순수 분리하는 것은 매우 어렵다고 알려져 있다(Isogai 등, 1998; Shikata와 Kitagawa, 1977). 그렇기 때문에 입자를 순수 분리하여 면역 동물인 토끼에 면역하였으나 항체 생성에 실패한 결과도 보고되어 있다(Boccard와 Milne, 1981). 따라서 본 연구에서는 RBSDV S10 N-말단의 단백질을 in vitro에서 발현시켜 이 단백질을 대량 배양한 후 정제된 단백질을 항원으로 항혈청을 제작하였다. 제작된 항혈청은 Western blot 및 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) 검정으로 역가를 확인하였다(Wang 등, 2006). RBSDV의 한국 분리주에 대한 항혈청 제작은 국내에서 최초로 보고되는 결과이다.
재료 및 방법
RBSDV S10-N (1-834 nt) RT-PCR, 클로닝
RBSDV-miryang 이병주로부터 게놈 dsRNA를 추출하여 RT-PCR의 주형으로 사용하였다(Uyeda 등, 1998). RT-PCR에 사용한 primer는 RBSDV-miryang S10 (GenBank JX994211) N-말단의 1-834 nt 부분을 대상으로 하여 forward (5’-GCAATTCCATATGGCTGACATAAGACTC-3’), reverse (5’-CCGCTCGAGATCCAAAACACTTAATTC-3’)로 하였으며 forward에 Nde I, Reverse에 Xho I 제한효소 사이트가 포함되게 설계하였다. 증폭된 cDNA를 발현벡터 pET-21a (Novagen, Madison, WI, USA)의 Nde I, Xho I 사이트에 클로닝하였다. 이 벡터는 발현 단백질의 nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid (Ni-NTA) affinity chromatography 정제를 위하여 N-말단에 6개의 histidine (His)을 가지고 있다. RT-PCR에 의해 증폭된 유전자를 클로닝하여 염기서열 분석으로 확인 후 S10 1-834 nt 부분의 발현을 실시하였다.
RBSDV S10 N (1-834 nt) 단백질 발현 및 정제
클로닝된 RBSDV S10-N 말단 1-834 nt (RBSDV S10-N [1-278 aa])를 Escherichia coli host BL21(DE3), BL21(DE3)pLysS, BL21(DE3)RIPL 3종에서 단백질 발현을 실시하였다(Chen 등, 2012). 발현조건은 isopropyl β-D thiogalactoside (IPTG) 최종농도 1 mM, lysis buffer A는 20 mM Tris, 10 mM NaCl (pH 8.0), buffer B는 50 mM NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl (pH 8.0)로 온도 20°C, 37°C에서 4시간 배양하여 optical density (OD)값이 0.5–0.6 정도가 되도록 하였다. 배양액을 12% polyacrylamide gel에서 전기영동하여 단백질 발현을 확인하였다. 발현이 확인된 E. coli (BL21(DE3)RIPL)를 최종 농도 1 mM의 IPTG로 발현을 유도하고 37°C에서 OD값이 0.5–0.6 정도 될 때까지 배양한 후 정제를 실시하였다. 단백질 정제는 lysis buffer (50 mM NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl, 8 M urea [pH 8.0]), washing buffer (10 mM NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl, 20 mM imidazole, 8 M urea [pH 8.0]), elute buffer (50 mM NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl, 100 mM imidazole, 8 M urea [pH 8.0])를 사용하여 Ni-NTA affinity column에서 실시하였다. Ni-NTA column에 binding된 추출물을 12% polyacrylamide gel 전기영동으로 대상 단백질을 확인하였다.
Western blot
발현된 대상 단백질을 확인하기 위하여 2가지 buffer 조건에서 induced cell 전체, induced cell 상층액, 추출물을 대상으로 Western blot을 실시하였다. Ni-NTA binding에 사용한 buffer는 lysis buffer (50 mM NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl, 8 M urea [pH 8.0]), washing buffer (50 mM NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl, 20 mM imidazole, 8 M urea [pH 8.0]), elution buffer (50 mM NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl, 250 mM imidazole, 8 M urea [pH 8.0])로 하였다. Western blot은 5% skim milk로 blocking하였으며 Tris-buffered saline with Tween buffer로 10분씩 3회 washing 후 첫 번째 항원은 1,000배 희석한 anti-his로 90분 반응시켰다. 10,000배 희석한 anti-mouse-horseradish peroxidase에 의해 1시간 반응 실시 후 detection solution으로 반응을 확인하였다.
ELISA 역가 검정
RBSDV S10-N (1-287 aa)의 발현 단백질을 항원으로 하여 면역 동물인 토끼에 주사하여 항혈청을 제작하였다(Abclon, Seoul, Korea). 항원을 토끼에 주사하기 전에 pre-immune serum을 채취하여 음성대조구로 사용하였다. 만들어진 항혈청을 이용하여 ELISA로 역가를 검정하였다(Wang 등, 2006). 항원량은 200 ng/well을 사용하였으며 만들어진 항체를 100–10,000배 희석하여 반응을 실시하였다. 반응 후 ELISA reader (PerkinElmer Victor X3, 450 nm; ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA)로 측정하였다. 본 연구는 중앙대학교 동물실험윤리위원회의 승인을 받았다(14-0051).
결과 및 고찰
RBSDV S10-N (1-834 nt) 클로닝
RBSDV-miryang isolate S10 (JX994211)의 N 말단 1-864 nt (1-278 aa) (Fig. 1)을 발현벡터인 pET-21a에 클로닝한 후 colony PCR을 실시하고 이중 3개의 클론에 대한 염기서열 분석으로 RBSDV S10-N (1-834 nt)을 확인하였다.
RBSDV S10 N (1-834 nt) 단백질 발현 및 정제
염기서열 분석으로 S10-N (1-834 nt)의 삽입이 확인된 클론을 사용하여 E. coli (BL21[DE3], DL21[DE3]pLysS, BL21[DE3]RIPL)에서 배양온도 20°C와 37°C에서 단백질 발현을 유도한 결과 BL21(DE3)와 BL21(DE3)RIPL에서 배양온도 37°C의 A, B buffer 조건에서 대상 단백질 (약 32.4 kDa)의 과다 발현된 밴드가 확인되었다(Fig. 2).
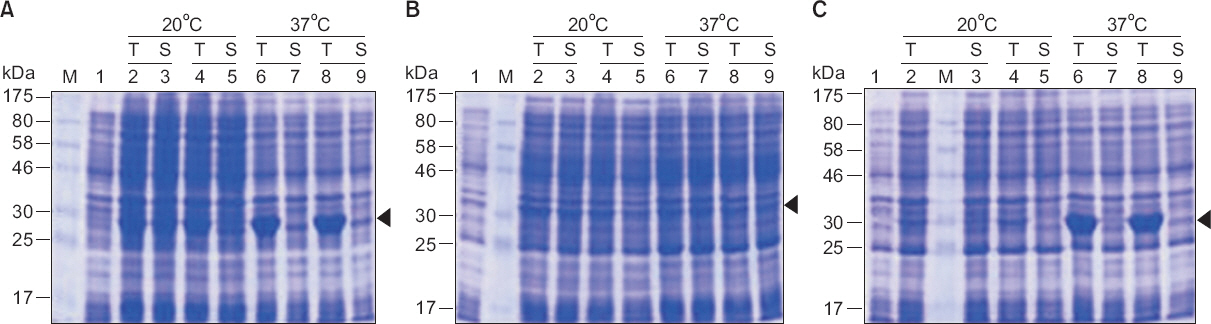
SDS-PAGE (12.5%) analysis of Rice black-streaked dwarf virus (RBSDV) S10-N (1-834 nt) expressed in Escherichia coli, stained with coomassie brilliant blue. Expression of RBSDV S10-N (1-834 nt) with isopropyl β-D thiogalactoside induction for 4 hours. Molecular mass markers (M) are indicated by the kDa values at the margin. (A) RBSDV S10-N (1-278) BL21(DE3). (B) RBSDV S10-N (1-278) BL21(DE3)pLysS. (C) RBSDV S10-N (1-278) BL21(DE3)RIPL. Lane 1: uninduced cell lysate total; lane 2, 6: induced cell lysate total; lane 3, 7: induced cell lysate supernatant; lane 4, 8: induced cell lysate total; lane 5, 9: induced cell lysate supernatant.
Ni-NTA binding test
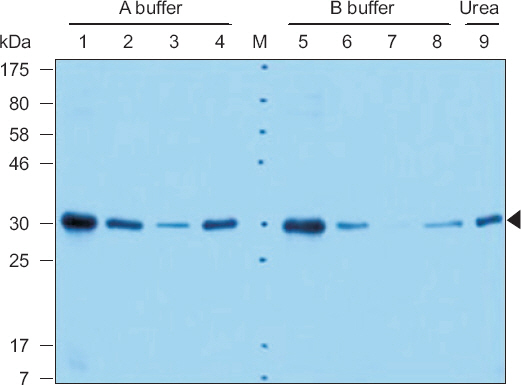
발현된 단백질을 native 조건에서 Ni-NTA binding test를 한 결과 A, B buffer 조건에서 대상 단백질의 정제는 확인이 불가능하였으므로, native 조건에서의 정제는 적합하지 않을 것으로 판단되어 denatured 조건에서 정제를 실시하였다. 그 결과 eluted faction에서 대상 단백질 위치인 약 32.4 kDa에서 정제된 band가 확인되었다(Fig. 3).

Nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid binding test of Rice black-streaked dwarf virus S10-N (1-834 nt) expressed in Escherichia coli at denatured condition. Molecular mass markers (M) are indicated by the kDa values at the margin. Lane 1: induced cell urea total (10 μl/1 ml), lane 2: induced cell urea supernatant (10 μl/1 ml); lane 3: flow-through (10 μl/1 ml); lane 4–6: wash 1–3 (10 μl/1 ml); lane 7–9: elute 1–3 (10 μl/1 ml).
Western blot
Ni-NTA binding test에서 추출된 단백질의 정제 여부를 Western blot으로 재확인한 결과 위의 모든 조건에서 대상 단백질이 확인되었다. 그러나 native condition binding test의 경우 A, B buffer 조건의 eluted fraction에서 정제된 대상 단백질이 확인되었으나 양이 매우 적고 elute fraction에서 대상 단백질 위치 외에 anti-his로 detection되지 않는 비특이적 밴드들 때문에 정제도가 낮아 native condition에서의 정제는 적합하지 않았다(data not shown). 그러나 denatured condition의 eluted fraction에서는 정제된 양이나 정제도 면에서 native condition보다 정제수율이 더 좋았다. 이상의 결과로 볼 때 RBSDV S10-N (1-834 nt)의 대상 단백질은 BL21(DE3)와 BL21(DE3)RIPL의 37°C 조건에서 과다 발현되었고, native 및 denature 조건에서 정제된 단백질이 확인되었으나 denature 조건에서 정제수율이 더 높은 것을 확인하였다(Fig. 4).
Western blot of Rice black-streaked dwarf virus S10-N (1-834 nt) at denatured condition. Molecular mass markers (M) are indicated by the kDa values at the margin. Lane 1, 5: induced cell total (2 μl/300 μl); lane 2, 6: induced cell supernatant (2 μl/300 μl); lane 3, 7: elute fraction 1 (2 μl/300 μl); lane 4, 8: elute fraction 1 (2 μl/300 μl); lane 9: urea elute 1 (2 μl/300 μl).
His-RBSDV S10-N (1-278) 정제
His-RBSDV S10-N (1-278 aa)을 위의 조건으로 1 l 배양 후 denatured condition에서 Ni-NTA affinity column 정제를 실시한 결과 washing buffer 및 100 mM imidazole elution buffer에서 정제된 단백질이 확인되었다. 250 mM imidazole elution buffer에서도 정제된 밴드가 확인되었으나 이미 100 mM에서 과량의 단백질이 elution되어 정제된 단백질의 양은 적었다(Fig. 5). 정제된 단백질이 확인된 wash fraction 및 100 mM elute fraction을 pooling하여 정량한 결과 BL21(DE3)RIPL에서 0.65 mg/ml (total 12 mg)의 단백질을 얻을 수 있었다(Fig. 6). 얻어진 단백질을 항원으로 RBSDV S10-N (1-278)에 대한 항혈청을 제작하였다.

Histidine Rice black-streaked dwarf virus S10 (1-278) purification with nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid affinity column at denatured condition. Molecular mass markers (M) are indicated by the kDa values at the margin. Lane 1: urea cell lysate total; lane 2: urea cell lysate supernatant; lane 3: flow-through; lane 4–8: wash 1–5; lane 9–13: 100 mM imidazole elute 1–5; lane 14–18: 250 mM imidazole elute 1–5.
ELISA 역가 검정 결과
정제한 RBSDV S10-N (1-287) 단백질을 항원으로 ELISA 테스트를 실시하였다. 항원을 토끼(New Zealand white)에 주사하기 전에 pre-immune serum을 채취하여 음성대조구로 하였으며 primary immunize는 항원을 complete freund’s adjuvant (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA)와 혼합하여 피하주사하고 4주 후 incomplete freund’s adjuvant와 혼합한 항원으로 1차 부스팅을 실시하였다. 1주 후 1차 혈청 1 ml를 채취하여 ELISA test를 실시하고 2주 간격으로 부스팅과 채혈을 실시하였다. 3차 부스팅 1주 후 토끼 심장으로부터 채혈하고 최종 혈청을 분리하여 ELISA 테스트로 확인하였다. ELISA 테스트 결과 역가가 1:10,000으로 확인되었다(Fig. 7).

Titers of the two Rice black-streaked dwarf virus (RBSDV) S10-N (1-287) polyclonal antibodies against RBSDV.
본 실험의 결과로 RBSDV N-말단의 1-834 nt의 in vitro 단백질 발현이 확인되었으며 이 단백질을 대량 배양하여 정제한 결과 0.65 mg/ml (total 12 mg)의 단백질을 얻을 수 있었다. 얻어진 단백질을 항원으로 RBSDV에 대한 항혈청 제작에 성공하여 금후 항혈청을 이용한 대량 진단이 가능하게 되었다. 최근에는 중국으로부터 애멸구가 비래하여 벼줄무늬잎마름병(Rice stripe virus, RSV)뿐 아니라 RBSDV의 돌발적인 발생도 우려된다. 이러한 상황에서 이 항혈청을 이용하여 애멸구의 보독충률 검정 등을 실시하고 보독충을 방제하여 바이러스 매개를 차단하면 RBSDV의 대발생을 조기에 방제할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by the National Institute of Crop Science (PJ01004204).

